India Insider: Booming GDP & Fragile Foundations of Growth
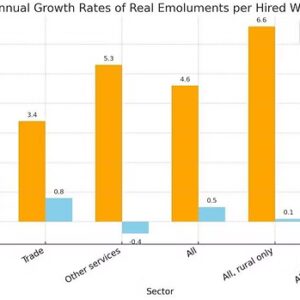
India’s economic footprint on the global stage is expanding significantly each year. As the world’s largest democracy, the nation achieved a remarkable 7.4% GDP growth rate January to March of this fiscal year. Yet, beneath this impressive headline, job creation remains tepid, overshadowed by slowing foreign direct investments (FDI) and lower corporate investments from India’s domestic market.
Despite Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s initiative to attract manufacturing into India and boost jobs, the manufacturing share of GDP has stubbornly clung to 16% for the last decade. While India’s services sector accounts around 55% of GDP, the IT and allied services sectors contributes a mere 3-4% of total employment. Even after the last two decades in which India’s Asian neighbors have shifted labor force out of agriculture and into high scale manufacturing, 45% of India’s workforce still are employed in agriculture and aligned services constituting only 15-17% of GDP.
Speculative Capital, Excessive Credit and Rising Financial Risk
Between 2003 and 2023, India attracted approximately $275 Billion USD from foreign capital inflows, encompassing mostly equity and debt foreign portfolio investments. These capital injections are speculative in nature, primarily chasing returns in financial markets, rather than being directly invested into long-term productive infrastructure like manufacturing and export oriented industries.
Interestingly, India’s public sector banks especially between 2008 and 2015 aggressively lent to infrastructure, real estate and capital intensive projects. The state owned banks tried to fill the gap left behind by private investors. A substantial share of these loans later turned into non-performing loans, exacerbating a duel crisis as corporate and bank balance sheets came under severe stress within a few years. The government of India stepped in and injected 3.1 lakh crore Rupees ($45 Billion USD) to recapitalize the struggling banks, and also orchestrated mergers of weaker banks with stronger banks. India’s citizens helped cover these costs via higher taxes and hidden banking charges.
Reserve Bank of India: FX Reserves and Liquidity Dynamics
As of financial year 2025, the RBI’S Foreign Exchange Reserves stand at around $696 billion USD. While a stronger reserve buffer is crucial for maintaining external stability, the Reserve Bank of India’s purchase of foreign currency to build reserves leads to problems with domestic Rupee liquidity and creates liabilities for the RBI’s balance sheet. Unless it’s not fully absorbed via Open Market operations, it will end up as excess liquidity in the banking system.
Post 2020 and the Covid19 pandemic, loose monetary policy and excess liquidity within the banking system has culminated with more reckless lending. Unsecured retail credit particularly in personal loans, credit cards and consumer finance is troubling. Non-banking financial companies (shadow banking) and fintech enterprises also expanded rapidly into this segment and now pose risks.
India Falling into Debt Trap
Per a recent survey conducted by the RBI, household financial savings have sharply declined to a five decade low of 5.1% of GDP in FY2023, down from 11.5% in 2021. Concurrently, household liabilities have risen, particularly in the unsecured credit segment.
Delinquencies in small ticket personal loans and “Buy Now, Pay Later“ programs are on the rise, prompting the RBI to intervene recently with tightening of personal loan norms in late 2023. This dynamic suggests that excessive credit creation, unaccompanied by productive or real income growth, is fueling a fragile boom in consumption backed predominately by debt especially among middle and lower income groups.
Lower Net Foreign Direct Investment amid Higher Repatriation
Even with coordinated efforts from the likes of Apple, Foxconn (Hon Hai Technology Group) and other electronics companies setting up facilities, and the assembly of manufactured goods like iPhones as part of the “China Plus“ strategy, a more comprehensive method of doing business and improved proactive FDI policy is needed. Overall results are still falling short. Evidence shows many companies continue to choose Vietnam and Mexico over India, which is clearly reflected in the lower net FDI figures in India’s Balance of Payments. In financial year 2024-25, net FDI fell 96% to $353 million USD, caused by a surge of money being repatriated out of India led by foreign companies, and also increased foreign investments by Indian companies to other nations, per the Hindu magazine.
The irony is that India needs foreign capital to finance its current accounts deficit, long-term capital investment would boost jobs and increase wages. As the central Indian government practices an austerity drive and its corporations show an unwillingness to invest, India needs higher foreign capital at this crucial juncture. How will India achieve this task? Without better employment and raising wages, India’s celebrated growth faces risks from underlying cracks.